AI 101
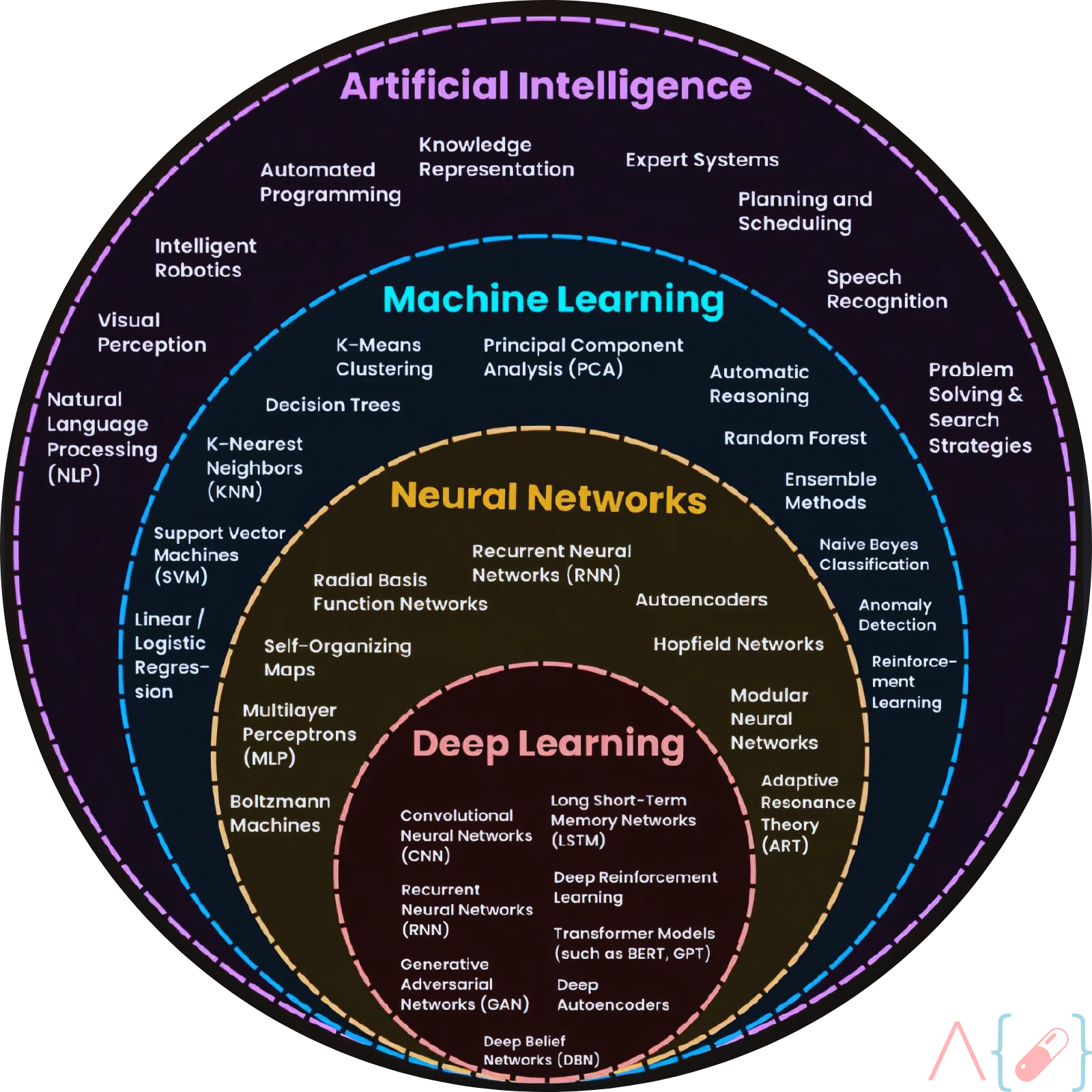
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a transformative technology that involves the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, particularly computer systems. These processes include learning, reasoning, and self-correction.
General AI
| Abbreviation | Term | Definition | Example | Resources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI | Artificial Intelligence | The ability of machines to exhibit intelligent behavior. | Self-driving cars, virtual assistants, medical diagnosis systems. | Artificial Intelligence |
| AGI | Artificial General Intelligence | A hypothetical form of AI able to understand or learn any intellectual task a human can. | Currently non-existent, imagine an AI writing scientific papers and holding debates. | Artificial General Intelligence |
| ASI | Artificial Superintelligence | AI surpassing human intelligence in all aspects. | Theoretical; potential dangers are debated by AI researchers. | Artificial Superintelligence |
| ANI | Artificial Narrow Intelligence | AI designed to perform specific tasks well within a single domain. | Chess-playing AI, spam filters, image recognition systems. | Artificial Narrow Intelligence |
| -- | The Turing Test | A test of a machine's ability to exhibit intelligent behavior indistinguishable from a human. | Historically controversial, but an AI convincingly passing the Turing Test would be a major milestone. | The Turing Test |
| -- | The Singularity | A hypothetical point when technological growth, led by AI, spirals beyond control. | Speculative, often in science fiction, but sparks debate about the long-term trajectory of AI. | The Singularity |
Machine Learning
| Abbreviation | Term | Definition | Example | Resources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ML | Machine Learning | Field of AI where computers learn without explicit programming, through analyzing data and patterns. | Spam filters, recommender systems, medical diagnosis, fraud detection | https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/glossary |
| DL | Deep Learning | A subset of ML using complex neural networks loosely inspired by the human brain. | Image classification, natural language processing, self-driving car perception | https://www.deeplearning.ai/ |
| NN | Neural Network | A mathematical model inspired by biological brains, forming the basis of many deep learning techniques. | Image recognition, language translation, stock market prediction | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_neural_network |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network | A type of NN especially effective for image and video processing | Facial recognition, object detection for self-driving cars, medical image analysis | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FmpDIaiMIeA |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network | A type of NN designed to process sequential data, like text or time series. | Machine translation, text summarization, stock price prediction | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Recurrent_neural_network |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network | A type of ML model where two networks compete, resulting in the ability to create realistic images, videos, or other data. | Creating realistic synthetic images for art or training datasets, generating realistic product photos | https://machinelearningmastery.com/what-are-generative-adversarial-networks-gans/ |
| RL | Reinforcement Learning | An ML type focusing on an agent learning through trial-and-error interactions with an environment. | Training robots to perform complex tasks, AI beating human champions in video games | https://spinningup.openai.com/en/latest/ |
| SL | Supervised Learning | An ML type where the model learns from a labeled dataset (input-output pairs). | Facial recognition (learning from labeled images of faces), spam filters (learning from labeled examples of spam and non-spam emails) | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Supervised_learning |
| UL | Unsupervised Learning | An ML type where the model finds patterns in unlabeled data. | Customer segmentation in marketing (identifying similar customer groups), anomaly detection in manufacturing | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unsupervised_learning |
| SSL | Semi-supervised Learning | An ML type using a combination of small labeled data and a larger amount of unlabeled data. | Medical image analysis (using some labeled samples, and many more unlabeled ones) improving speech recognition | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Semi-supervised_learning |
| -- | Overfitting | When a machine learning model learns the training data too closely, failing to generalize to new examples. | An image classifier recognizing specific training images perfectly but poorly on unseen images | https://aws.amazon.com/what-is/overfitting/ |
| -- | Transfer Learning | Reusing knowledge gained from one ML task to improve performance on a related task. | Pre-trained language model fine-tuned for specific industry tasks, saving time and data | https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/images/transfer_learning |
| -- | Probabilistic Reasoning | A type of reasoning that takes into account uncertainty. | Used in decision-making AI systems where outcomes are not certain, like weather prediction or medical diagnosis. | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Probabilistic_reasoning |
| -- | Bayesian Reasoning | A method of reasoning that uses probability theory to make inferences. | Updating a spam filter after seeing new emails, robot navigation in unknown environments. | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bayesian_inference |
| -- | Genetic Algorithms | A type of ML algorithm inspired by evolution, used to solve complex optimization problems | Finding optimal product shipment routes, designing efficient neural network architectures. | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genetic_algorithm |
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
| Abbreviation | Term | Definition | Example | Resources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NLP | Natural Language Processing | Computers understanding, interpreting, and manipulating human language. | Chatbots, sentiment analysis, machine translation, text summarization | https://nlp.stanford.edu/ |
| NLU | Natural Language Understanding | An NLP subfield focusing on a computer's ability to read and understand text as a human would. | Machines summarizing news articles, virtual assistants answering complex questions | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Natural_language_understanding |
| NLG | Natural Language Generation | An NLP subfield focusing on computers coherently producing human-like text. | Automatic article writing, chatbots generating creative responses, composing personalized marketing emails | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Natural_language_generation |
| -- | Sentiment Analysis | Detecting the underlying emotions (positive, negative, neutral) within text. | Businesses analyzing customer feedback on social media, tracking brand perception over time | https://monkeylearn.com/sentiment-analysis/ |
| -- | Machine Translation | Automatically translating text from one language to another. | Google Translate, enabling cross-border communication, translating online product reviews | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Machine_translation |
| -- | Text Summarization | Condensing a long piece of text into a shorter version while retaining key information. | News article summarizers, creating abstracts of research papers | https://huggingface.co/transformers/task_summary.html |
| -- | Named Entity Recognition (NER) | Identifying and classifying named entities (people, organizations, locations) in text. | Extracting important information from news articles or legal documents | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Named-entity_recognition |
| -- | Topic Modeling | Discovering abstract topics that occur within a collection of documents. | Analyzing large datasets of customer reviews to identify common themes or issues. | https://towardsdatascience.com/topic-modeling-and-latent-dirichlet-allocation-in-python-9bf156893c24 |
| -- | Speech Recognition | The ability of computers to understand human speech. | Virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa, automated transcription services. | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Speech_recognition |
Computer Vision (CV)
| Abbreviation | Term | Definition | Example | Resources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CV | Computer Vision | Enabling computers to see and interpret the visual world, similar to human vision. | Object detection, image classification, facial recognition, autonomous robots | https://opencv.org/ |
| OCR | Optical Character Recognition | Converting images of typed, handwritten, or printed text into machine-readable text data. | Scanning documents, extracting text from street signs in self-driving cars, reading handwritten forms | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Optical_character_recognition |
| -- | Image Segmentation | Partitioning an image into meaningful regions or objects. | Medical image analysis (identifying tumors), separating foreground from background in photos for editing | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image_segmentation |
| -- | Object Detection | Locating and identifying objects within an image or video. | Self-driving cars detecting pedestrians and traffic signs, robots locating items to pick in a warehouse, facial recognition systems | https://www.mathworks.com/discovery/object-detection.html |
| -- | Image Classification | Assigning labels to images based on their content. | Sorting photos by type (landscape, portrait, etc.), medical image diagnosis (identifying different types of tumors) | https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/images/classification |
| -- | Pose Estimation | Determining the position and orientation of a person or object in an image or video. | Motion capture for animation in movies, tracking body movements in fitness applications | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wEoyxE0GP2M |
| -- | 3D Reconstruction | Creating a 3D model of an object or a scene from images or videos. | Applications in architecture (modeling buildings), augmented reality (placing virtual objects) | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/3D_reconstruction |
Hardware
| Abbreviation | Term | Definition | Example | Resources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPU | Tensor Processing Unit | ASICs (Application Specific Integrated Circuits) designed by Google, optimized for deep learning workloads. | Accelerating the training of large AI models, particularly neural networks, often used in Google's data centers | https://cloud.google.com/tpu |
| GPU | Graphics Processing Unit | Originally for graphics rendering, now widely used to accelerate ML tasks due to parallel processing power | Training deep neural networks, processing images and videos, cryptocurrency mining | https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/ |
| LPU | Large Language Model Processing Unit | Emerging hardware specifically designed to handle the vast computational demands of large language models (LLMs). | Aiming to process LLMs more efficiently than TPUs or GPUs, particularly for conversational AI tasks | (Still in early development - Keep an eye on AI hardware news) |
| FPGA | Field-Programmable Gate Array | A type of integrated circuit that can be reconfigured after manufacturing, offering flexibility for specialized AI acceleration. | Prototyping new AI chip designs, accelerating low-latency AI inference in edge devices | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Field-programmable_gate_array |
| CPU | Central Processing Unit | The general-purpose "brain" of a computer, capable of running various AI algorithms, though often with less efficiency than specialized hardware. | Used for smaller AI models, AI tasks alongside general computing, or in devices where a dedicated accelerator is not cost-effective | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Central_processing_unit |
Large-Scale Models (VLM, LLM)
| Abbreviation | Term | Definition | Example | Resources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VLM | Vision Language Model | Deep learning models capable of processing both images and text. | Generating image descriptions, answering questions about images, creating art based on text descriptions | https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.05782 (Example research paper) |
| LLM | Large Language Model | Extremely powerful language models, trained on massive datasets of text, that can generate text, translate languages, write different kinds of creative content, and answer your questions in an informative way | ChatGPT, Google's Bard, Jurassic-1 Jumbo, other similar conversational AI tools | https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt/ |
| -- | Transformer Architecture | The neural network architecture underlying most LLMs and many VLMs, enabling them to process sequential data effectively. | Self-attention mechanism in Transformers allows models to focus on relevant parts of text or images, improving their understanding | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hYdO9CscNes (Explanatory Video) |
| -- | Multimodal Models | Models capable of processing and generating data of different modalities (e.g., text, image, audio) | A model translating image descriptions into different languages, or generating a video clip based on a textual script | https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.05782 |
| -- | Prompt Engineering | The art of crafting prompts (instructions or input text) to get the best results from LLMs. | Phrasing questions specifically, providing examples, or using keywords can influence the LLM's response style and accuracy | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prompt_engineering |
AI Techniques & Concepts
| Term | Definition | Example | Resources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Mining | Extracting meaningful patterns and insights from large datasets. | Businesses analyzing customer data to identify purchasing trends, scientific research finding patterns in genetic data | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_mining |
| Embeddings | Mathematical representations of words or concepts, often used in NLP and recommendation systems. | Representing a word like "cat" as a numerical vector, where similar words have similar vectors | https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/text/word_embeddings |
| Knowledge Representation | Techniques for how AI systems store and organize information. | Semantic networks, ontologies used to represent relationships between concepts, knowledge graphs powering search engines | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Knowledge_representation_and_reasoning |
| Search Algorithms | Methods used by AI systems to explore problem spaces and find solutions. | A* search algorithm used for pathfinding in games and robotics, beam search for machine translation | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Search_algorithm |
| Expert Systems | AI systems that emulate the decision-making ability of a human expert in a specific domain | Medical diagnosis systems, financial risk assessment tools, systems guiding technicians through troubleshooting processes | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Expert_system |
| Robotics | The integration of AI into robots and other physical devices. | Autonomous warehouse robots, self-driving cars, robotic arms in manufacturing | https://www.robotics.org/ |
| Bias (in AI) | Unfair or prejudicial outcomes resulting from AI decisions | Facial recognition systems misidentifying certain ethnicities more often, algorithms biased against certain groups when making loan decisions | https://www.ibm.com/blog/shedding-light-on-ai-bias-with-real-world-examples/ |
| Explainable AI (XAI) | Field focused on making the decisions of AI systems more transparent and understandable to humans. | Tools for identifying which features of the input were most important for an AI model's decision, techniques for explaining why an image was classified a certain way | https://www.darpa.mil/program/explainable-artificial-intelligence |
| AI Ethics | Moral and social implications of AI, including fairness, transparency, accountability, and potential dangers. | Ongoing discussion of safety protocols for self-driving cars, safeguards against biased AI in hiring, regulation of autonomous weapons | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ethics_of_artificial_intelligence |
| Fuzzy Logic | A type of logic that allows for uncertainty and partial truth. | Controlling air conditioning systems, making self-driving car decisions in ambiguous situations. | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fuzzy_logic |
| Pattern Recognition | A fundamental ability for many kinds of AI tasks. | Identifying objects in images, detecting fraudulent transactions, classifying types of music. | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pattern_recognition |
| Recommender Systems | Systems recommending products or services to users based on their patterns and data. | Netflix suggesting movies you might like, Amazon recommending products to buy. | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Recommender_system |
| Symbolic AI | A classic approach to AI, using symbols and rules to represent knowledge, contrasting with data-driven methods. | Expert systems for medical diagnosis (in the past), AI systems designed to play chess. | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Symbolic_artificial_intelligence |
Key Terms and Definitions
A
- Algorithm: A set of rules or instructions given to an AI system to help it learn and make decisions.
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): A type of AI that can understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks, similar to human intelligence.
- Artificial Neural Network (ANN): A computing system inspired by the biological neural networks that constitute animal brains, used in machine learning.
B
- Backpropagation: A method used in neural networks to calculate the gradient of the loss function and update the weights to minimize errors.
- Big Data: Large and complex data sets that traditional data processing software cannot handle efficiently.
C
- Chatbot: An AI application that can simulate a conversation with users through text or voice interactions.
- Computer Vision: A field of AI that enables computers to interpret and make decisions based on visual data from the world.
D
- Deep Learning: A subset of machine learning involving neural networks with many layers, capable of learning from large amounts of data.
- Decision Tree: A model used in machine learning that splits data into branches to make decisions based on certain conditions.
E
- Expert System: An AI program that uses a knowledge base of human expertise to solve specific problems within a particular domain.
F
- Feature Extraction: The process of transforming raw data into a set of features that can be used for machine learning.
G
- Generative Adversarial Network (GAN): A class of machine learning frameworks where two neural networks compete to improve the accuracy of generated data.
H
- Hyperparameter: A parameter whose value is set before the learning process begins and controls the behavior of the learning algorithm.
I
- Inference: The process of making predictions or decisions based on a trained machine learning model.
J
- Jupyter Notebook: An open-source web application that allows users to create and share documents containing live code, equations, visualizations, and narrative text.
K
- K-Means Clustering: A method of vector quantization used for cluster analysis in data mining.
L
- Logistic Regression: A statistical model used for binary classification that predicts the probability of a binary outcome.
M
- Machine Learning (ML): A subset of AI that involves training algorithms to learn from and make predictions based on data.
N
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): A field of AI that focuses on the interaction between computers and humans through natural language.
O
- Overfitting: A modeling error in machine learning where a model learns the training data too well, including noise and outliers, leading to poor performance on new data.
P
- Predictive Analytics: The use of data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning techniques to identify the likelihood of future outcomes based on historical data.
Q
- Quantum Computing: A type of computing that uses quantum-mechanical phenomena, such as superposition and entanglement, to perform operations on data.
R
- Reinforcement Learning: A type of machine learning where an agent learns to make decisions by taking actions in an environment to maximize cumulative reward.
S
- Supervised Learning: A type of machine learning where the model is trained on labeled data, meaning the input comes with the correct output.
T
- TensorFlow: An open-source machine learning framework developed by Google for building and training neural networks.
U
- Unsupervised Learning: A type of machine learning where the model is trained on unlabeled data and must find patterns and relationships within the data.
V
- Validation Set: A subset of data used to tune the parameters of a machine learning model to prevent overfitting.
W
- Weights: Parameters within neural networks that are adjusted during training to minimize the error in predictions.
X
- XGBoost: An optimized distributed gradient boosting library designed to be highly efficient, flexible, and portable.
Y
- YOLO (You Only Look Once): A real-time object detection system that processes images in a single pass to identify objects.
Z
- Zero-shot Learning: A type of machine learning where the model can recognize objects or perform tasks without having seen any examples during training.
This glossary can be useful for:
- Anyone who wants to learn more about AI.
- AI researchers and professionals who want a quick reference.
- Educators and students who are teaching or learning about AI.
Notes:
- AI is a rapidly evolving field, so new terms and definitions may be created over time.
- There may be multiple definitions for the same term.
- It is important to consider the context when using AI terminology.
I hope you find this glossary helpful!